Traumatic Brain Injury in Teens
Traumatic brain injuries (TBI) are a significant concern for teens, especially those involved in contact sports like football and gymnastics. During these critical years of development, a TBI can impact cognitive skills, academic performance, and social interactions. Early diagnosis and targeted therapies are essential to support recovery and ensure teens can continue to grow and thrive both in school and in their personal lives. Our specialized programs are designed to address the unique needs of teens, promoting brain health and helping them achieve their full potential.

Concussions are mild Traumatic Brain Injuries and can have detrimental impact on your teen’s brain, treat it seriously. Let us help.
What Activities have Resulted in Traumatic Brain Injury in Teens
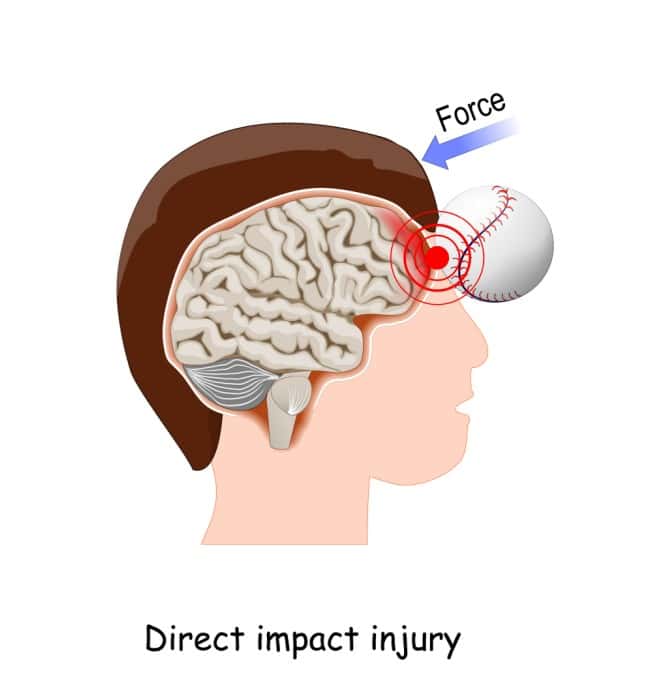
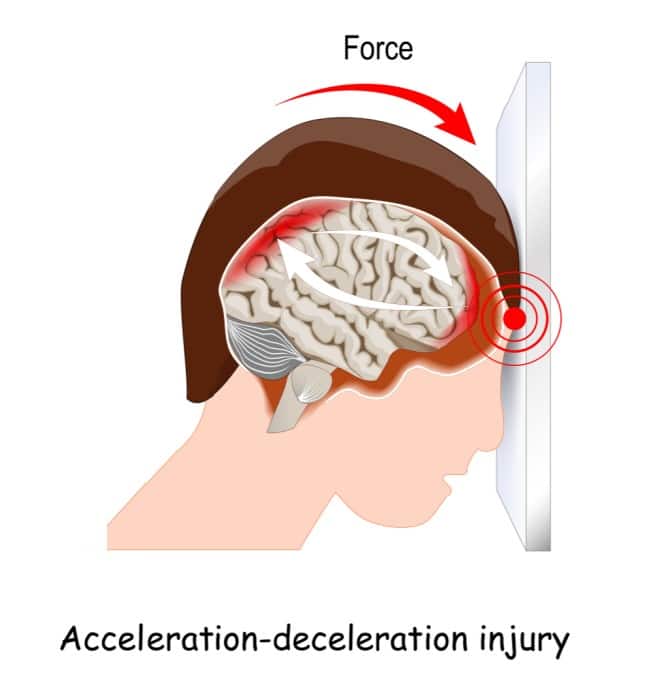
If your teen has ever sustained a concussion and is now experiencing symptoms, you may benefit from neurological support. There are many ways teens sustain concussions, mild, moderate, and severe traumatic brain injuries and evidence recommends treatment because this is a time of critical brain development.
Contact Sports: Sports like football, soccer, hockey, and rugby involve physical contact and can result in head injuries.
Gymnastics: Falls and missteps during routines can lead to significant impacts.
Cheerleading: High-flying stunts and falls can cause head injuries.
Biking and Skateboarding: Falls and collisions while biking or skateboarding can result in TBIs.
Car Accidents: Teens are at risk for TBIs from car accidents, especially if not wearing seat belts.
Physical Fights: Altercations can lead to blows to the head.
Horseback Riding: Falls from horses can cause severe head injuries.
Symptoms of Traumatic Brain Injury in Teens to take Seriously
Daily Life Activities and School
+ Difficulty Concentrating: Teens may struggle to focus on homework, follow classroom instructions, or complete tasks that require sustained attention.
+ Memory Problems: Forgetting assignments, misplacing items, or having trouble recalling information learned in class.
+ Headaches: Frequent headaches that can interfere with daily activities and school attendance.
+ Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or lacking energy, making it hard to participate in after-school activities or complete homework.
+ Mood Changes: Increased irritability, anxiety, or depression, which can affect relationships with friends and family.
+ Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or sleeping too much, impacting overall well-being and school performance.
+ Sensitivity to Light and Noise: Being easily bothered by bright lights or loud sounds, which can make it challenging to be in busy environments like classrooms or social events.
Transition to Adult Responsibilities
+ Organizational Difficulties: Struggling to plan and manage tasks, such as scheduling appointments or managing time effectively.
+ Reduced Problem-Solving Skills: Finding it hard to make decisions or solve problems, which can affect job performance and everyday adult responsibilities.
+ Emotional Regulation Issues: Difficulty controlling emotions, leading to inappropriate responses in social or work situations.
+ Decreased Social Skills: Challenges in maintaining relationships, networking, and effectively communicating in personal and professional settings.
+ Physical Coordination Problems: Ongoing issues with balance and coordination, affecting the ability to perform certain job tasks or drive safely.
+ Academic or Job Performance: Lower academic achievements or job performance due to cognitive and emotional challenges stemming from the TBI.
